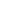
At sea, ships navigate in waves. At this time, the ship is subjected to added wave resistance, and at the same time, it is in motion, consuming extra energy than in calm water. This test is performed by generating waves in a tank to measure the added wave resistance and the ship's behavior in such waves.
Seakeeping Test
 Unlike testing in calm water, resistance acting on the hull in waves increases due to the effect of waves. Since wave conditions vary depending on the sea area in which a ship is to operate, we set wave conditions (wave height and wavelength) for the model ship and conduct resistance tests at the assumed ship speed to determine the increase in hull resistance under wave conditions.
Unlike testing in calm water, resistance acting on the hull in waves increases due to the effect of waves. Since wave conditions vary depending on the sea area in which a ship is to operate, we set wave conditions (wave height and wavelength) for the model ship and conduct resistance tests at the assumed ship speed to determine the increase in hull resistance under wave conditions.

 Ship motions are measured in navigating at an assumed speed in head sea conditions. The measured motions have three degrees of motion: heave, pitch, and surge.
Ship motions are measured in navigating at an assumed speed in head sea conditions. The measured motions have three degrees of motion: heave, pitch, and surge.